
Medicine and food having the same origin
The theory of "medicine and food having the same origin" posits that many foods and medicines do not have an absolute dividing line between them. Ancient medical scholars applied the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) concepts of "four properties and five flavors" to food, believing that each type of food also possesses these attributes. This concept dates back to the era of Shen Nong, when there was no distinction between medicine and food; substances were used based on whether they were toxic or non-toxic.
In TCM, the theory suggests that in ancient times, medicine and food originated together but diverged over thousands of years. However, there may be a return to the concept of using food as medicine or replacing medicine with food. All animals, plants, and minerals fall within the broad category of TCM, with the difference between drugs and food mainly lying in dosage and side effects.
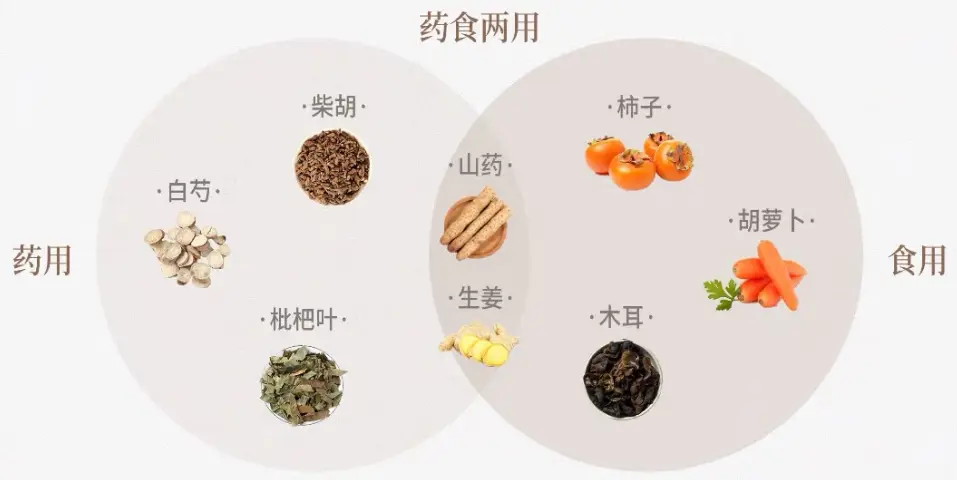
Dual-use of medicine and food
Since ancient times, traditional Chinese medicine has had the theory of "medicine and food are of the same origin", which means that many foods are drugs, and there is no absolute boundary between them according to the provisions of the Food Safety Law,
Once a certain Chinese medicinal herb is explicitly included in the list of medicinal and edible homology, it is also allowed to be added to daily food for use.

Origin
In the Tang Dynasty medical book "Huangdi Neijing", it is written that
“Eating on an empty stomach is medicine for illness”
It means that it can be used as a food ingredient when you want to satisfy your hunger, and as a medicinal herb when you are sick

Characteristic
It will have certain medicinal properties
There is no limit on consumption, and long-term consumption is also acceptable
Can be used as a production ingredient for ordinary food, containing rich nutrients
The medicine and food around us are of the same origin

Mint
Relieve wind and heat, clear and benefit the leader, regulate qi and relieve depression

Hawthorn
Digestive and healthy stomach

Jujube
Supplementing the middle and nourishing qi, nourishing blood and generating fluids

Red bean
Promote diuresis and reduce swelling

Ginger
Relieve symptoms and dispel cold, prevent colds

Papaya
Beauty and skincare, healthy and balanced diet
Until now, the list of both food and medicine includes
Clove, star anise, sword bean, cumin, thistle, yam, hawthorn, purslane, Zaocys dhumnades, prunus mume, papaya, hemp seed, daidaihua, polygonatum odoratum, liquorice, angelica dahurica, ginkgo, white lentil, white flat tofu pudding, longan meat (longan), cassia seed, lily, nutmeg, cinnamon, yuganzi, bergamot, almond (sweet and bitter) Jujube, black jujube), siraitia grosvenorii, plum kernel, honeysuckle, green fruit, houttuynia cordata, ginger (ginger, dried ginger), trifoliate orange chessboard, medlar, gardenia, amomum villosum, pandahai, tuckahoe, citron, elsholtzia chinensis, peach kernel, mulberry leaf, mulberry, tangerine, platycodon grandiflorum, euzhiren, lotus leaf, radish seed, lotus seed, galangal, light bamboo leaf, light lobster sauce, chrysanthemum, chicory, yellow mustard, yellow essence Perilla frutescens, perilla seeds, kudzu root, black sesame seeds, black pepper, locust seeds, locust flowers, dandelions, honey, Chinese fir seeds, jujube seeds, fresh white fescue roots, fresh reed roots, pit vipers, orange peels, mint, Job's tears seeds, Allium macrostemon, raspberry, patchouli, Angelica sinensis, hawthorn, saffron (also known as "saffron" in spices and seasonings), grass fruit, turmeric, long pepper, Codonopsis pilosula, Cistanche deserticola (desert), Dendrobium officinale, American ginseng, Astragalus membranaceus, Ganoderma lucidum, Cornus officinale, Tianma, Eucommia ulmoides leaves.